The Doppler effect
The Doppler effect, named after C. Doppler, arises in moving acoustic sources. When a acoustic source moves relative to a listener, a shift in the received frequency and wavelength is observed. Thus, the frequency of the received wave is:
\[f_{rec}=f_{src}\frac{c_0+v_r}{c_0+v_s} \]
where \( f_{rec}\) is the received frequency, \( f_{src}\) is the source frequency, \(c_0\) is the sound speed \(v_r\) the velocity of the moving receptor and \(v_s\) the velocity of the moving source.
Doppler effect for \(v_s=0.6c_0\)

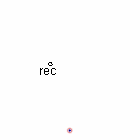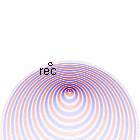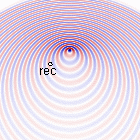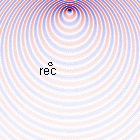
Doppler effect for \(v_s=\frac{1}{2}c_0\)

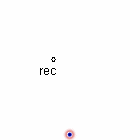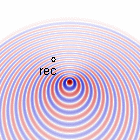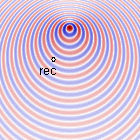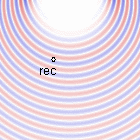
Doppler effect for \(v_s=[\frac{1}{20},\frac{1}{5},\frac{1}{3}]c_0\)



Supersonic sources: doppler effect for \(v_s=[1.02, 1.1, 2]c_0\)


